TreeExplorer
24 November 2025
Shows all drives, folders and files as a tree structure
and has a versatile context menu.
- Maintain, eject, partition, or shred disks
- Copy or mirror folders or drives
- Create reports on PCs, WLAN, storage devices or USB devices
- Cmd or Powershell with the selected path
Although TreeExplorer was designed for maintenance tasks,
it can also be useful in daily work:
For example, the 'Offline' command can be used to disconnect a USB stick
before safely removing it.
No admin rights are required for this.
1 Download
By downloading TreeExplorer you agree to the End User License Agreement.

|
|
||||||||
TreeExplorer is part of the Reuschtools container.
After installing Reuschtools,
TreeExplorer can also be launched from the Start Menu.
2 Features
-
TreeExplorer does not require admin rights.
If a particular command requires admin rights, they will be requested when the command is launched. - Displays hidden drives and folders and can open them in Windows® Explorer if needed.
- If a Windows® drive is mirrored, the target Windows® will be made bootable.
- Free of any charges.
- Anonymous download.
- No hidden downloads, uploads or updates.
- No setup required (Click To Run).
3 Disadvantages
-
Unlike CopyWin,
no check is performed before mirroring a Windows® drive
to see if the target drive's partitioning is suitable for a Windows® boot.
Therefore, if necessary, use the commands
'GPT Partition' or 'MBR Partition' from the TreeExplorer context menu before starting the mirroring process.
4 Screenshots
4.1 Dark Contrast
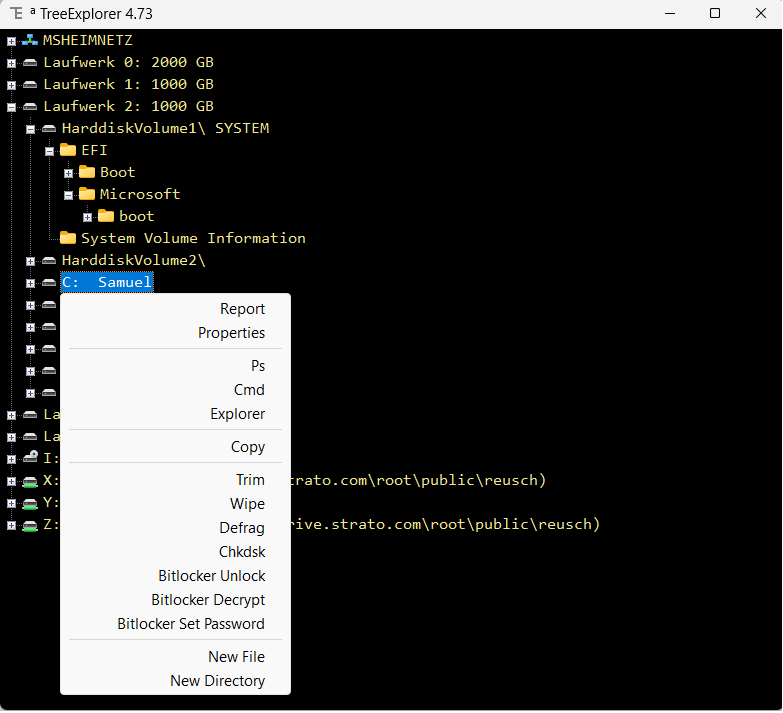
5 Instruction
5.1 Copy and Paste or Copy and Mirror
Both 'Paste' and 'Mirror' compare the destination with the source.
The destination is updated accordingly.
This makes both commands very fast during an update.
For both commands, you first select a folder or drive with 'Copy'.
5.1.1 Paste
The 'Paste' command copies the source into the destination.
Copy(C:\test1\MyFolder) -> Paste(D:\)
Copies the contents of C:\test1\MyFolder into D:\MyFolder
Copy(C:\) -> Paste(D:\)
Copies the contents of drive C:\ into the folder D:\Drive_C
5.1.2 Mirror
The target of a 'Mirror' command, however, can only be a drive.
The 'Mirror' command copies the source into the same path
on the target drive.
Copy(C:\test1\MyFolder) -> Mirror(D)
Copies the content of C:\test1\MyFolder into D:\test1\MyFolder
Copy(C:\) -> Mirror(D)
Mirrors drive C:\ to drive D:\.
After mirroring, the content of D:\ is identical to the content of C:\.
If a Windows® is located on C:\,
the new Windows® on drive D:\ will be made bootable.
The source drive does not need to be the currently booted Windows® drive
to be recognized as a Windows® system by 'Mirror'.
To mirror a Windows® drive, the 'Restore access control'
switch should be enabled.
This is the default setting for drives.
Back mirroring is also possible.
If the current Windows® is located on drive C:\
and a previous copy of Windows® is located on drive D:\, then:
Copy(D:\) -> Mirror(C)
will restore the previous copy to drive C:\.
After successfully mirroring, Windows® must be restarted.
5.2 Command Line
treeexplorer_4.74_english.exe -x rtcmd tree C:\test1\MyFolder
Start TreeExplorer and open the folder 'C:\test1\MyFolder'.
5.3 Remote
treeexplorer_4.74_english.exe \\PC2 rtcmd tree
Start TreeExplorer for PC2
The command must be started with admin rights.
This command only works if you are either the main administrator on PC2,
or if you have set
LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy on PC2.
The command works with Windows® Home or Pro on PC2,
and with 32-bit or 64-bit versions.
6 Support
Please send suggestions for improvement and bug reports to
